Diabetic Supplements: Myth or Fact?
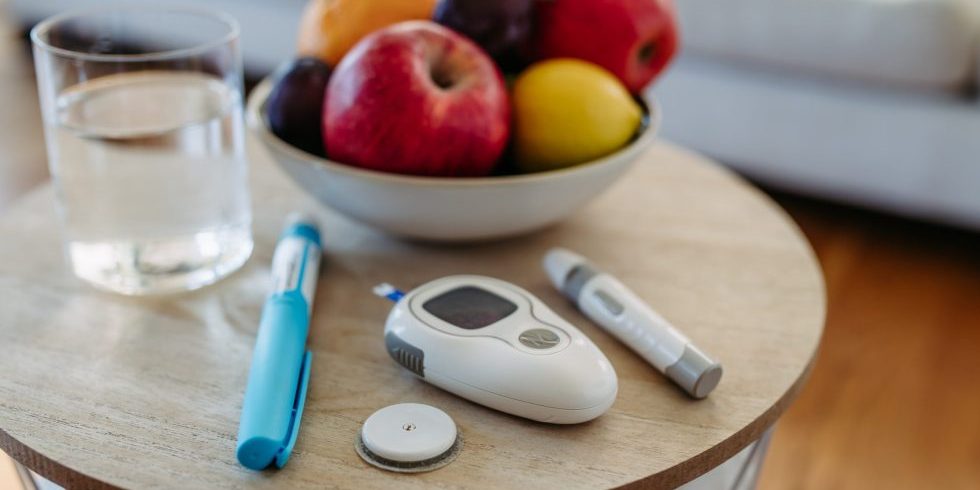

Imagine sitting with friends, chatting about health. One excitedly shares a story about a magical supplement that claims to lower blood sugar, overnight. They say one pill lets you enjoy your favorite desserts worry-free, and the room buzzes with intrigue.
That’s a myth.
While a quick fix for diabetes sounds great, it oversimplifies the issue. Managing diabetes needs a balanced diet, regular exercise, and, if needed, medications (Mayo Clinic, 2024). It must be confusing as there are so many choices out there, that might make you want to try it all. Let’s find out what medications that can help you with diabetes.
What is Diabetes?
Before discussing specific medications, it’s important to know that diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or doesn’t use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels (WHO, 2023). If unmanaged, this can cause serious complications like heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve problems.
There are two main types of diabetes:
For many people with diabetes, lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise are crucial. However, medication often plays an equally important role in managing blood sugar levels.
Are Diabetes Supplements a Myth?
Now that we’ve covered commonly prescribed medications, let’s discuss diabetic supplements. With many options available, it’s crucial to differentiate between what is right and what is wrong. Over-the-counter supplements like cinnamon, chromium, and alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) claim to lower blood sugar, but are they effective?
| Cinnamon | Some studies suggest that cinnamon may help improve insulin sensitivity, but the evidence is inconsistent (Mayo Clinic, 2023). It’s not a replacement for medication. |
| Chromium | Cefalu and Hu (2004) discuss that this mineral is thought to improve insulin action, but again, research is mixed, and it’s unlikely to make a significant difference without other interventions. |
| Alpha-Lipoic Acid | WebMD (2024) states that this antioxidant may help with diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain), but more research is needed to confirm its benefits for blood sugar control. |
Instead of relying on supplements, try adding tasty, healthy snacks to your day. Based on the American Diabetes Association (n.d.), fruits for diabetics like berries, apples, and citrus are nutrient-rich and can help keep your blood sugar in check. They’re delicious and generally lower in sugar than sweetened snacks.

Prescription Medications for Diabetes
Rybelsus 14mg Tablet 30s
- What is it?
Rybelsus contains semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist that helps lower blood sugar by boosting insulin production and reducing sugar release from the liver. - How does it work?
It’s one of the few oral GLP-1 medications, prescribed for adults with Type 2 diabetes, often alongside other meds. - Fact or Myth?
Fact. Rybelsus is proven to manage blood sugar and may promote weight loss for some individuals.
Forxiga 10mg Tablet
- What is it?
Forxiga (dapagliflozin) is an SGLT2 inhibitor that helps the kidneys remove excess glucose through urine. - How does it work?
It lowers blood sugar by preventing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys and reduces the risk of heart failure in Type 2 diabetes patients. - Fact or Myth?
Fact. Forxiga is clinically proven to manage blood sugar and offers cardiovascular benefits.
Hovid Glimaryl 2mg Tablet
- What is it?
Hovid Glimaryl contains glimepiride, a sulfonylurea that stimulates the pancreas to release more insulin. - How does it work?
It lowers blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production, making it a popular choice for Type 2 diabetes. - Fact or Myth?
Fact. Glimepiride effectively controls blood sugar but may cause hypoglycemia, so monitoring is important.
Proglutrol G2 2/500mg SR Tablet
- What is it
Proglutrol G2 combines glimepiride (2mg) and metformin (500mg), a first-line treatment for Type 2 diabetes. - How does it work?
The combination boosts insulin production and reduces glucose production, making it effective for blood sugar control. - Fact or Myth?
Fact. Both glimepiride and metformin are well-researched, and their combination offers better blood sugar control than either alone.
Clamide 5mg Tablet 100s
- What is it?
Clamide contains glibenclamide (glyburide), a sulfonylurea that stimulates insulin release from the pancreas. - How does it work?
It lowers blood sugar by boosting insulin production. - Fact or Myth?
Fact. Glibenclamide is an effective option for managing blood sugar in Type 2 diabetes, though it carries a risk of hypoglycemia.
So, Myth or Fact?

When managing diabetes, prescription medications are proven to be essential for many people with Type 2 diabetes. Some supplements might help a little, but they shouldn’t replace your meds or healthy habits like diet and exercise. Always check with your doctor before including any supplement in your diabetes care plan.
In short, prescription medications are grounded in science and are critical for managing diabetes, while most supplements are still in the realm of myth when it comes to their effectiveness. Stick to what’s proven, and work closely with your healthcare team to find the best regimen for you.
References
- World Health Organization. (2024). Diabetes. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
- Castro, M. R. (2024). Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar? Mayo Clinic. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). https://www.mayoclinic.org
- Cefalu, W. T., & Hu, F. B. (2004). Role of chromium in human health and in diabetes. Diabetes Care, 27(11), 2741–2751. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.11.2741
- Saling, J. (2024, June 27). Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA). WebMD. Medically reviewed by Jabeen Begum, MD. https://www.webmd.com/
- American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Fruit. Health & wellness. American Diabetes Association. Retrieved November 12, 2024, from https://www.diabetes.org/nutrition/healthy-food-choices-made-easy/fruit
FAQ
Supplements may help manage diabetes, but they should not replace a healthy diet or prescribed medications. Supplements like cinnamon, berberine, and alpha-lipoic acid have shown potential to help lower blood sugar levels. However, always talk to your doctor before starting any supplement, as they may interact with your medications.
Berberine is often considered one of the most effective supplements for lowering blood sugar. It may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver. Other supplements like cinnamon, chromium, and alpha-lipoic acid can also support blood sugar control.
Blood sugar support pills can have side effects, including digestive issues, diarrhea, nausea, or low blood sugar (if taken with medications like insulin). Supplements like alpha-lipoic acid or berberine may cause mild stomach upset in some people. Always consult your doctor to avoid interactions with other medications.
Currently, there is no cure for diabetes, but it is manageable. Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy, while type 2 diabetes can be controlled through lifestyle changes, medication, and in some cases, surgery (like bariatric surgery). Research into stem cells and other treatments is ongoing, but a cure is not yet available.
Diabetes patients should be cautious with supplements like ginseng, licorice, or high doses of vitamin C, as they may interfere with blood sugar control or interact with diabetes medications. Always check with your healthcare provider before taking any new supplement.
Vitamins that can help repair nerve damage, especially in diabetics with neuropathy, include:
- Alpha-lipoic acid
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Folic Acid
Alpha-lipoic acid should be avoided by individuals with thyroid disorders, those on chemotherapy, or those taking certain medications that might interact with it, like diabetes medications (especially insulin). Always consult your doctor before taking it.
Yes, Neurobion, which contains B-vitamins (B1, B6, and B12), can be beneficial for diabetics, especially those with diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage). However, always check with your doctor before taking it, especially if you are on other medications.
There is currently no complete cure for diabetes. However, some people with type 2 diabetes can manage and sometimes even achieve normal blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and weight loss, under medical supervision.
Stem cell research for diabetes is still in early stages. In theory, stem cells could help regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, offering a potential treatment for type 1 diabetes. However, this is still experimental and not yet a proven cure.












