Fungal Acne vs Bacterial Acne: How to Tell & Treat
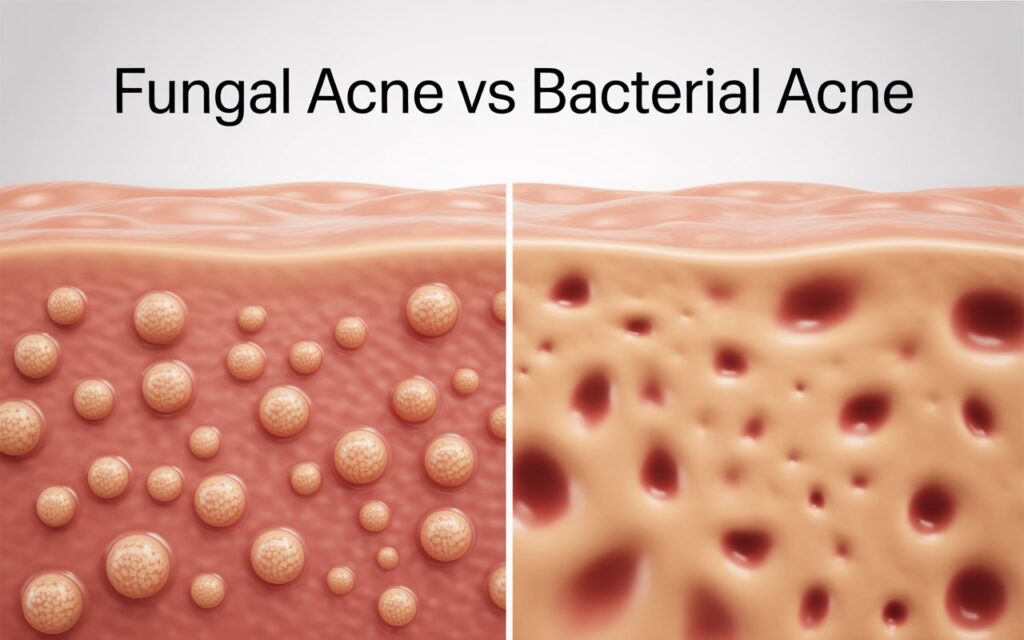
The fact that acne can be frustrating itself is frustrating, but when the treatment does not work, you have a possibility that it is not that you think. Numerous individuals mix up the concepts of Fungal Acne vs Bacterial Acnes but the two differ in terms of reasons behind the diseases, display, and the most suitable treatment. Learning these differences and the time to consult a dermatologist via a teleconsult can be the only difference between having a clear, healthy skin.
What Is Fungal Acne?
Malassezia folliculitis, which is also called fungal acnes, is not acne. It is a proliferation of a Malassezia yeast, a form of fungus that grows on the skin. This yeast can cause inflammation in clusters when it grows in hair follicles which will result in a bunch of itchy acne-like spots.
Malassezia Cues: How to Identify It
- Fungal acne: Itchy uniform bumps: Unlike bacterial acne, fungal acne is usually presented in the form of small, itchy pustules and papules that are very similar in size.
- Common on the upper part of the body: It often appears on the chest, the back, and the shoulders, and even on the forehead, where the sweat and oil can be found.
- Instigated by humidity and sweat: Fungal acne is an organism that grows well in a warm humid climate.
- Makes it worse with antibiotics: As antibiotics are directed at the bacteria, it may destabilize the microbiome of the skin enabling Malassezia to prosper.
What Is Bacterial Acne?
Cutibacterium acnes (previously Propionibacterium acnes) is the cause of the type of bacteria acnes most commonly known to people, bacterial acne. It develops when there is overproduction of oil, dead skin and bacteria that block the pores leading to the development of blackheads, whiteheads, and swollen pimples.
Key Signs of Bacterial Acne
- Varied lesion types: You may see a mix of blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, or even cysts.
- Painful, deep pimples: Bacterial acne can form tender nodules beneath the skin.
- Typically on the face: While it can occur on the back or chest, it’s most common in oil-rich facial zones (T-zone, cheeks, jawline).
- Responds to antibiotics or acne topicals: Unlike Fungal Vs Bacterial Acne often improves with benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or prescription antibiotics.
Fungal vs. Bacterial Acne: The Diagnostic Differences
| Feature | Fungal Acne (Malassezia folliculitis) | Bacterial Acne (C. acnes) |
| Cause | Yeast (Malassezia) overgrowth | Bacteria (C. acnes) |
| Appearance | Small, uniform, itchy bumps | Mixed-size pimples, often painful |
| Common Areas | Chest, back, shoulders, forehead | Face (T-zone, cheeks), back |
| Itchiness | Common | Rare |
| Response to Antibiotics | Worsens | Improves |
| Response to Antifungal Treatments | Improves | No effect |
What to Avoid If You Have Fungal Acne
The aim of dealing with fungal acne is to suppress the presence of excess oil and yeast. Certain skincare materials may aggravate the condition.
Avoid:
- Heavy oils: Malassezia may be fed by coconut oil, olive oil, and other occlusive oils and worsen breakouts.
- Fatty moisturizers or thick sunscreens: Choose lightweight and non-comedogenic, non-oil products.
- Sweaty clothing: Change after work out clothes immediately and ensure that the skin is dry.
Rather, seek ingredients that have the label of Fungal-Acnes safe or oil free.
Good remedies to Fungal acne
Antifungal Washes
Apply body cleansers or body washes that contain active antifungal agents. Common options Include:
- Ketoconazole 2% wash (Nizoral®)
- Selenium sulfide hair shampoo (Selsun Blue®)
- Zinc pyrithione soap
Apply as a daily bath on the affected parts, leave several minutes after which they can be washed.
Topical or Oral Antifungals
In case the bumps are not cleared by over-the-counter washes, a dermatologist might prescribe:
- Topical antifungal creams: Clotrimazole or ketoconazole.
- Oral antifungal agents: Fluconazole or itraconazol in resistant ones.
Bacterial Acnes Treatment
In case of bacterial acne, a combination approach is usually suggested by the dermatologists:
- Benzoyl peroxide in order to inhibit bacterial growth.
- Salicylic acid to unclog pores.
- Knowledge: topical retinoids on skin cell turnover.
- Moderate to severe cases oral antibiotics or hormonal therapy.
When to Book a Teleconsult
In case you are not sure what kind of acne you are dealing with, or a specific condition is not responding to standard treatments, a teleconsult appointment with a dermatologist is a good idea. A specialist will be able to:
- Identify Malassezia Cues
- Prescribe particular antifungal/ antibacterial therapy.
- Safely change your skincare routine.
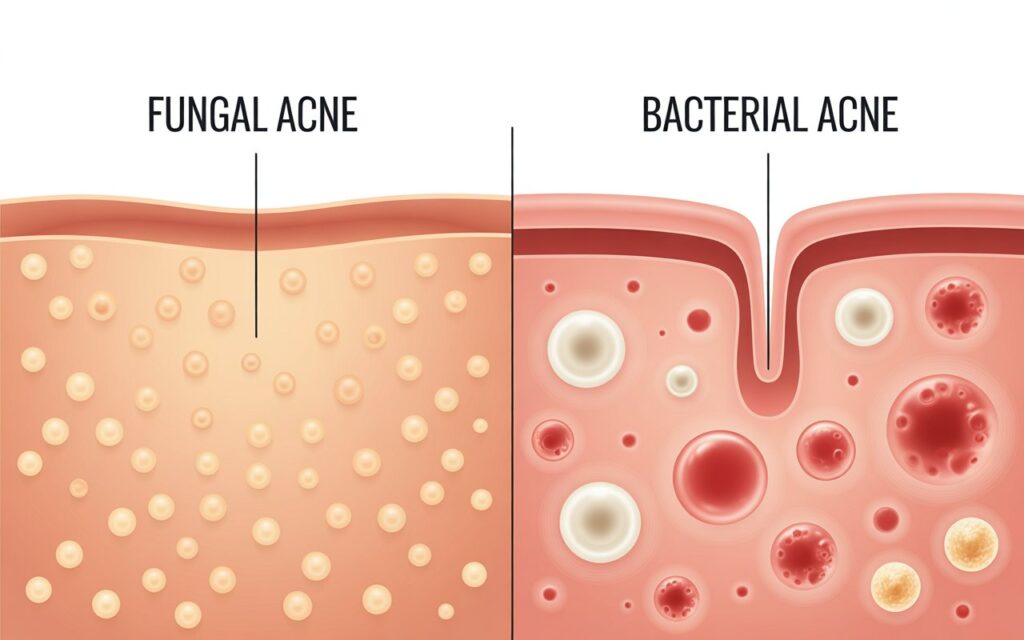
The Bottom Line
Although fungal and bacterial acne may appear similar, there are distinct differences in the causes and the treatments of the two. Note the specifics – including itchiness, uniformity of lesions, and the locations of the breakouts to inform your actions. It can be avoided by using Avoid Heavy Oils, preferring Antifungal Washes Or Lotions in case of Malassezia suspicion, and not hesitating to obtain a Professional Diagnosis Through Teleconsult.
If you’re dealing with persistent or unclear breakouts and aren’t sure whether it’s fungal or bacterial acne, For expert in-clinic consultations, visit Nexus Clinic. also You can book a teleconsultation with certified dermatologists through trusted platforms like DoctorOnCall for a personalized assessment, accurate diagnosis, and tailored treatment plan — including antifungal or antibacterial options suited to your skin’s needs.
FAQs
What causes acne?
The clogged pores, bacteria, hormonal changes, and genetics can cause acne.
Can I get acne medication online in Singapore?
Yes. Once we get online, our physicians will be able to recommend HSA-approved therapy – including topical ointments and oral antibiotics.
How soon will I see results?
The improvements that can be seen among most patients are evident after 4-8 weeks of regular treatment.
Are the treatments safe for sensitive skin?
Yes. Our doctors will tailor the treatment to your skin type to avoid irritation.
Do I need to see a dermatologist?
Not necessarily. Our doctors in Singapore can treat the mild to moderate acnes; the severe cases might be directed to a dermatologist.
Will delivery be discreet?
Yes. Your privacy is preserved by using plain and unmarked packaging of the medications.
People Also Ask
How to 100% remove acne?
Keep your face clean.
Wash your face with benzoyl peroxide face wash that is available over-the-counter one or two times in a day. This lowers the inflammation and eliminates bacteria related to the development of acne. And be sure to wash all the makeup and dirt off to make sure it does not accumulate and clog your pores.
What is the very best treatment for acne?
Tetracycline, minocycline and doxycycline are some of the common antibiotics used to treat acnes. These are the ones that are suitable in the case of moderate to severe acne. Isotretinoin (Amnesteem 2, Claravis and Sotret): Isotretinoin is an oral retinoid. Isotretinoin reduces the size of oil glands making them part of the formation of the acne.
What kills acne fast?
Benzoyl peroxide.
This substance destroys bacteria that cause acne, it assists to eliminate excess oil in the skin and exfoliation of dead skin cells that may block the pores. Benzoyl peroxide products over the counter are available 2.5% to 10 in strength.
What are 5 causes of acne?
The risk factors of acne are:
- Age. All individuals can develop acne though it is most prevalent during teenage years.
- Hormonal changes. This may result in such changes in puberty or pregnancy.
- Family history. Genetics plays a role in acne. …
- Greasy or oily substances. …
- Squeeze or rubbing on your skin.
What if my acne won't go away?
- Best Overall: Briogeo Destined for Density Peptide Shampoo. …
- Best Strengthening: Paul Mitchell Tea tree Scalp Care Anti-Thinning Shampoo.
- Best hair thickening shampoo: Kérastase Densifique Thickening Shampoo. …
- The Sensitive Scalp: Vegamour Gro+ Advanced Balancing Shampoo.
- Best in Volume: Ouai Fine Hair Shampoo.













